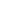
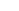
The machined cast iron is a highly durable and long-working life type of metal material. It’s forged by melting iron and molding it into various shapes and components. Machined cast iron parts are found in many places because of their high strength. This article covers the advantages of machined cast iron, its manufacturing process, how it is made, how strong it is and machined cast iron applications.
That makes machined cast iron not only a very good material for a lot of applications but also a favored choice compared to others. The primary advantage is its power. Machined cast iron can take quite a load and not snap. This is perfect for components that need to be wear-resistant. And machined cast iron is not prone to rust, allowing it to be used long-term without excessive maintenance.
This steel, however, is actually an iron produced by a foundry process known as casting. This revolves around heating a piece of iron until it reaches a molten state before being poured into a mold to take the desired form. After the iron cools down and is hardened, the iron is removed from the mold and formed into the final part. Making the iron to shape is called machining. This ensures that the machined cast iron parts are of the correct dimensions and shape.

So, the process of making machined cast iron includes several steps, It starts when the iron is melted in a furnace at extremely high temperatures. The melted iron is then poured into a prepared mold, which has been treated to prevent it from sticking. They put the iron in a mold and let it cool and harden for a while. Once hardened, it is removed from the mold, and any excess pieces are cut off. The final step is machining: taking the rough cast iron and forming it to what its needed to fit.

Machined cast iron components are incredibly strong and long-lasting. That is attributable to the high carbon content of cast iron, this makes it hard and wears resistant. Machined cast iron parts can carry heavy loads and perform well at high temperatures without cracking. This makes them ideal for use in machines engines and other areas when strength is of paramount importance. They also dampen vibrations, so they're suitable for projects that require stability.

Many industries use machined cast iron components. One case in point: car engines. After all, machined cast iron engine blocks and cylinder heads are strong and heat resistant, too, which is perfect for fast cars. Cast iron machined is also used to produce heavy equipment and machines for construction. It is also used to make cookware, pipes and other household products.
Our machined cast iron is part of our company, which allows us to integrate production and commerce. We can offer lower pricing and better quality than the majority of our competition. We cut out the middleman and give our customers competitive prices, higher quality products, and direct from the factory.
More than 100 customers have been helped by us, providing fast, accurate and effective solutions. We can meet a machined cast iron of client needs regardless of whether it's full customization or design-based customization. We make sure that every custom-designed project is executed in the most professional manner.
Our automated production lines CNC machines and surface treatment workshops work in tandem to help support machined cast iron We have the manufacturing capability to accommodate requirements of any size with the same production standards
Our customer service team is always available making sure that inquiries are responded to within a matter of hours quotations are sent within 6 hours and custom solutions can be delivered within machined cast iron Whatever time or place our customers reach out to us we will respond promptly and offer professional assistance making sure their needs are satisfied quickly